Orchestrating Data for Seamless Commerce Experiences
Written by
Marie Standeven
Published on
Aug 05, 2025
Businesses are adopting headless commerce and API-first strategies to build their digital experiences. And for good reason: these approaches offer great flexibility and agility. But they also bring new challenges to the table: fragmented data, complex integrations, and the heavy lift of manually coordinating many backend services. Simply decoupling the frontend isn't the full solution. The real trick, and where the true power lies, is in how backend systems orchestrate data to deliver a truly unified customer experience.
That's precisely the challenge Broadleaf Commerce tackles. Our platform, built on a modular, API-first architecture, uses smart orchestration services to simplify data management and make complex commerce flows work better. In this post, we'll show you how Broadleaf orchestrates data for key customer touchpoints (think Product Detail Pages or PDPs, and checkout), turning what could be a messy backend into truly engaging user journeys.
The Essence of Headless Commerce and API-First Design
At its core, headless commerce separates the presentation layer (what the customer sees) from the backend commerce logic (what powers the experience). This decoupling offers immense freedom over branding and allows businesses to innovate quickly on the customer experience across various frontends, including web, mobile, and even IoT devices. However, headless alone doesn't guarantee a modular or scalable backend system.
API-first design complements headless by making sure all platform features and data are accessible through clear, standardized APIs from the start. This foundational approach simplifies building custom experiences and integrating external systems. It's a requirement for effective headless and composable commerce, though it doesn't dictate how the system's services are structured internally or deployed.
While both headless and API-first are important for modern commerce, they address how to expose and present, not necessarily how to manage internal data across a complex microservices landscape. This is where the need for strong orchestration becomes essential.
The Power of Orchestration Services in Broadleaf
In a microservices architecture, data and business logic are distributed across many specialized services. Without a coordinating layer, frontend applications would need to make many complex calls to various services and then piece together the information themselves. This is where Broadleaf's orchestration services step in.
An orchestration service in Broadleaf is a service-layer component primarily designed to gather or process data from multiple other resource-tier services. Importantly, these services generally do not maintain their own persistent data layer, focusing instead on their main aggregation and coordination duties.
Why Orchestration is Essential
- Consolidated Responses: Orchestration services reduce the number of requests a frontend application needs to make by providing a single, comprehensive response, even when the data originates from multiple backend microservices.
- Complex Data Hydration: They handle the complexity of building data hierarchies and pulling information from disparate sources (e.g., combining product details with dynamic pricing, relevant offers, and digital assets).
- Backend for Frontend (BFF): Broadleaf's orchestration services often serve as a BFF layer, making client-server interactions more straightforward. This includes managing CORS, centralizing traffic, fire-walling services from a security perspective, and supporting advanced proxy flows like anonymous tokenization. Without proper orchestration, agility at the frontend can lead to "backend friction," resulting in operational inefficiencies and increased risk.
The Role of Providers
Within Broadleaf's orchestration services, providers are service-layer components specifically designed to communicate with external or underlying microservices. They abstract away the complexities of direct API calls, letting the orchestration logic focus solely on data aggregation and business process flow. Providers usually interact via service-to-service API calls, replacing the repository and data layers that would normally be found in other service types. Broadleaf's external providers typically use Spring WebClient for communication between services.
Customer Experiences in Action: PDP and Checkout Flows
Let's explore how orchestration services bring smooth customer experiences to life in two core commerce flows: the Product Detail Page and the Checkout process.
A. Product Detail Page (PDP) Orchestration
The main purpose of PDP orchestration is to provide a comprehensive, consolidated data response for a storefront application, filling it with all necessary product information for display.
Key Service: Catalog Browse Service
The Catalog Browse Service is a dedicated orchestration service that simplifies requests for commerce-facing applications to various catalog-related microservice APIs. It aims to reduce the number of requests needed to build browse, search, and product detail pages.
The PDP Flow:
- A frontend application requests data from the Catalog Browse Endpoint, for example, a call made to /catalog-browse/product/details.
- The Catalog Provider, an external provider component within the Catalog Browse Service, forwards this request to the ProductDetailsEndpoint of the core Catalog Service.
- Within the Catalog Service, the Product Details Service retrieves the basic product information using the provided URL or ID.
- Next, ProductDetails Contributors within the Product Details Service are triggered. These contributors are responsible for enriching the core product data by pulling in additional information such as variants, product options, included products, digital assets (images, videos), product tags, and navigational breadcrumbs. Specifically, AdvancedTagsProductDetailsContributor adds merchandising tags, and DataDrivenEnumsProductDetailsContributor adds data-driven enumerations like brand or merchandising type. This makes sure all relevant product aspects are brought together.
- At the same time, the Catalog Provider also interacts with the Pricing Provider (which in turn talks to the Pricing Services) to retrieve and provide the most accurate pricing information for the product, considering any dynamic or personalized pricing rules. This includes fetching retail, sale, or contract prices.
- Finally, a comprehensive ProductDetails response is assembled and returned to the frontend. This response includes all necessary data points: product details, advanced tags, assets, breadcrumbs, options, variants, and complete pricing information.
This orchestrated flow greatly reduces frontend complexity by delivering a single, rich data payload, removing the need for multiple, sequential API calls from the client side.
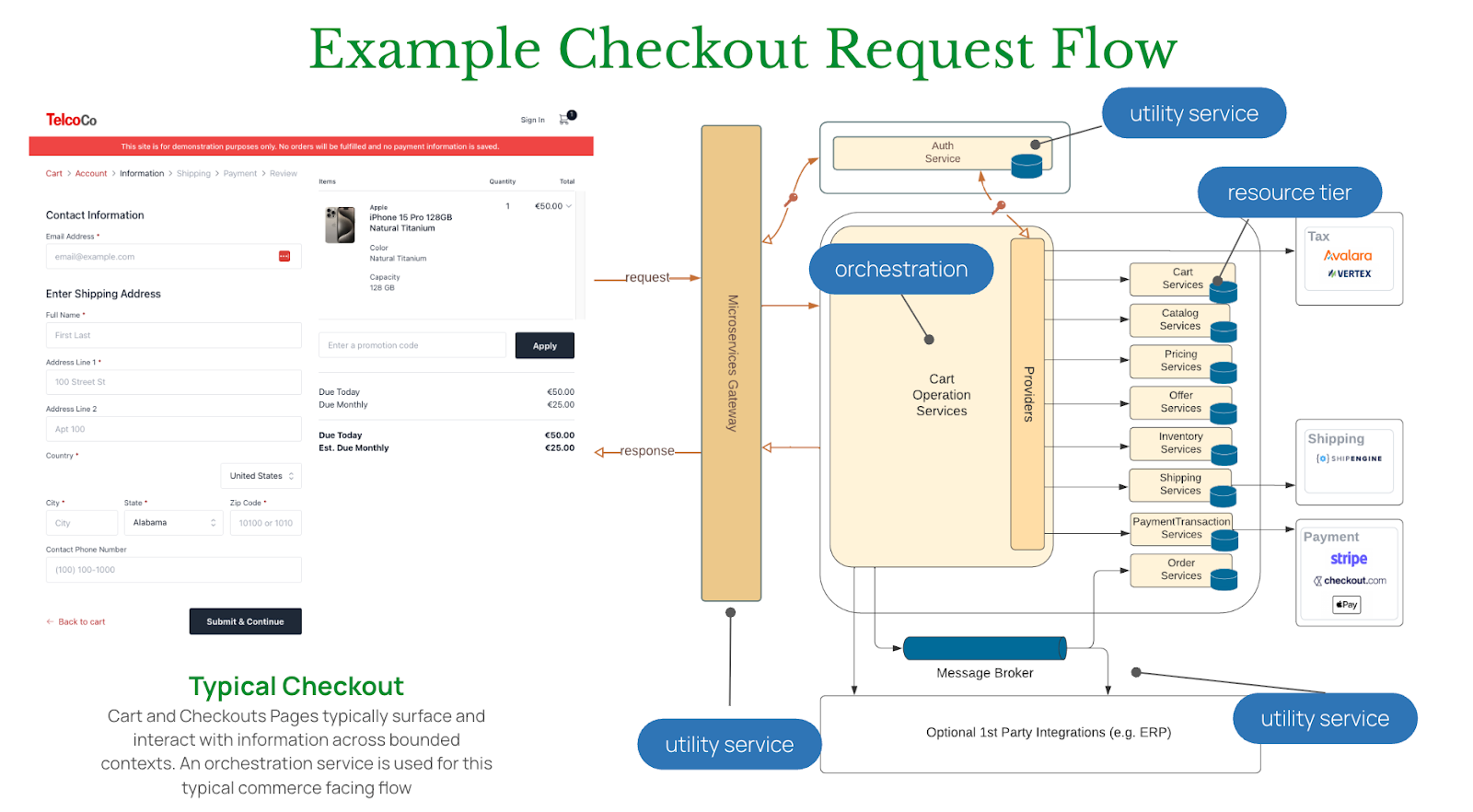
B. Checkout Flow Orchestration
The checkout process is complex by nature, needing strong orchestration to manage interactions across many internal and external services. Broadleaf's Cart Operation Services are central to this orchestration.
Key Service: Cart Operation Services
The Cart Operation Services acts as the core component, orchestrating various workflows for cart operations. It delegates to providers as needed to handle operations that involve external services such as fetching catalog, pricing, or inventory information.
The Checkout Flow in Action (Simplified):
Add to Cart:
- A request from the frontend (e.g., adding an item to the cart) is sent to the ManageCartEndpoint of the Cart Operation Services.
- The Cart Operation Service uses CartResolverService to find the correct cart for the user.
- It then calls the Catalog Service (via the ExternalCatalogProvider) to add detailed product information to the new cart item, keeping data integrity from a trusted source. The CartItemConfigurationService validates that cart items include all necessary selections and data.
- Next, the Inventory Service (via the ExternalInventoryProvider) engages to validate product availability and to optionally perform a "soft" reservation of the item's stock.
- The comprehensive pricing workflow is triggered, involving the DefaultCartPricingService, which uses the ExternalPricingProvider and ExternalOfferProvider to calculate prices, apply discounts, and factor in any promotions. The CartItemMergingService handles merging or rejecting similar items.
- Finally, the updated cart object with all its validated and priced items is stored back in the Cart Service (via the ExternalCartProvider).
Submit Checkout:
- When a customer is ready to finish their purchase, a request is sent to the CheckoutCartEndpoint.
- The DefaultCheckoutService starts the core Checkout Workflow, which first checks that the cart's status is valid for checkout (IN_PROCESS or CSR_OWNED).
- This workflow runs an ordered list of CheckoutWorkflowActivities responsible for important pre-submission checks. These include CartItemValidationActivity (required attributes, min/max quantities), CartFulfillmentValidationActivity (making sure necessary fulfillment info is present), CartPricingValidationActivity (all items have been priced), and CartStalePricingValidationActivity (making sure prices are up-to-date). The PaymentTransactionExecutionActivity is the final key step, responsible for executing authorization transactions for all unconfirmed payments.
- After all the checkout activities have successfully processed the cart, DefaultCheckoutService finalizes the checkout updating the cart such that its state and the state of its payments are now immutable (via the ExternalPaymentProvider & ExternalCartProvider).
- Upon successful completion of checkout finalization, a "checkout completion event" message is published to the checkoutCompletionOutput message channel.
- Downstream services, such as Order Services (which creates the final order record in the OMS) and Inventory Services (which converts soft inventory reservations into hard, permanent adjustments), take in this message to finalize the transaction.
This advanced orchestration makes sure that complex transactional logic, external system integrations (e.g., tax, shipping, payment gateways), and vital data consistency are managed smoothly and reliably.
The Strategic Advantage of Orchestrated Microservices
While the detailed flows of a PDP or checkout show immediate functional gains, the true strategic worth of a strong orchestration layer goes much deeper. In a composable commerce world, businesses want agility and the freedom to innovate without vendor lock-in or the burden of constantly rebuilding core functions.
Broadleaf’s orchestration services are a main support here. By bringing together different data and business logic from many microservices, they greatly simplify the complexity developers face at the frontend. This straightforward interaction allows development teams to work faster and focus on creating engaging user experiences, rather than struggling with backend data coordination.
Beyond that, orchestration offers important control and adaptability. It helps businesses manage a modular ecosystem more easily, providing flexibility in deployment and scaling that can adjust to different team structures, budget considerations, or even seasonal business demands. This architecture supports growth and change, ensuring the platform can meet future needs and strategic shifts without forcing expensive re-platforming efforts. It’s about building a commerce foundation that respects the developer's craft and solves real architectural pain points, allowing for true innovation and maintainability.
Conclusion
In the changing landscape of digital commerce, simply adopting headless or API-first technologies isn't enough. Real enterprise agility and the delivery of smooth customer experiences depend on strong backend orchestration. Broadleaf's API-first, modular microservices architecture, combined with powerful orchestration services, is built to meet this demand directly.
By making complex data flows simpler for everything from detailed product displays to intricate checkout processes, Broadleaf helps businesses turn backend complexity into effective customer journeys. This approach provides the flexibility to build, customize, and scale, making sure your commerce platform is not just current but ready for what's next. Explore Broadleaf Commerce to see how our approach can help your business reach its full potential.